-
1. Introduction to Six Sigma
-
2. Core Principles of Six Sigma and Lean
-
3. Six Sigma Methodologies
-
4. Six Sigma Tools and Techniques
-
5. The Belt System and Roles in Six Sigma
-
6. Metrics and Measurement
-
7. Implementing Six Sigma Across Industries
-
8. Benefits and Challenges of Six Sigma
-
9. Certification and Professional Development
-
10. Real-World Case Studies
-
11. Advanced Topics and Future Trends
-
12. Glossary and Key Terminology
6.2 Lean Metrics
Lean metrics focus on measuring and improving process efficiency by identifying and eliminating waste. These metrics provide insights into the overall performance of a process and help organizations achieve operational excellence by optimizing flow, reducing delays, and improving value delivery to customers.
1. Cycle Time
- Definition: The total time taken to complete a process, from the beginning of production to the final product or service delivery.
- Formula:
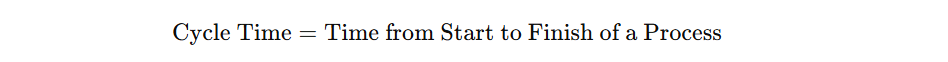
- Purpose: Measures the efficiency of a process by determining how quickly a unit can be produced.
- Importance: A reduction in cycle time indicates increased process efficiency and faster customer delivery.
- Application: Used to identify bottlenecks and opportunities to streamline processes.
2. Lead Time
- Definition: The total time it takes from receiving an order to delivering the product or service to the customer.
- Formula:

- Purpose: Measures the responsiveness of a process and how quickly customer demands are fulfilled.
- Importance: Shorter lead times increase customer satisfaction and reduce inventory costs.
- Application: Helps businesses to meet customer expectations and improve order fulfillment speed.
3. Throughput
- Definition: The number of units processed or produced in a given time period.
- Formula:
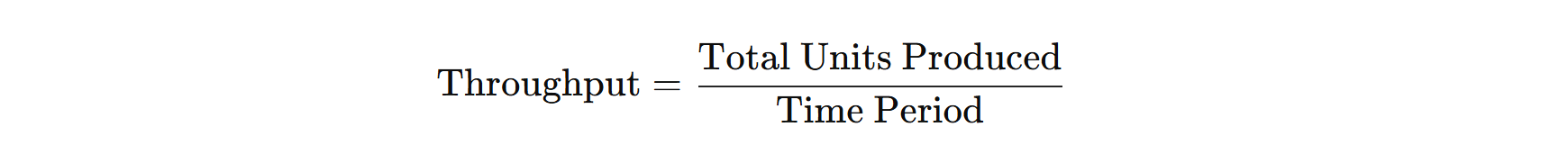
- Purpose: Measures how much work is being done within a specific timeframe.
- Importance: Increased throughput means higher production capacity and better resource utilization.
- Application: Helps in evaluating the overall production output and identifying opportunities for increasing efficiency.
4. Inventory Turnover
- Definition: The rate at which inventory is used or sold over a specified period.
- Formula:
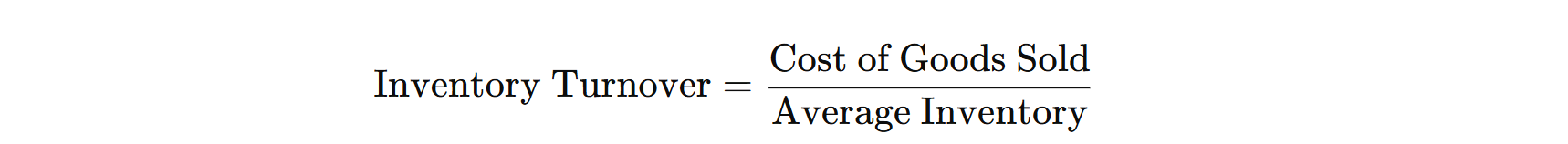
- Purpose: Measures how efficiently inventory is being managed and utilized.
- Importance: A higher inventory turnover rate indicates better inventory management, leading to cost savings and less capital tied up in unsold stock.
- Application: Used to optimize inventory levels and reduce excess stock.
5. First Pass Yield (FPY)
- Definition: The percentage of products or services that meet quality standards without requiring rework or correction.
- Formula:

- Purpose: Measures the efficiency of a process in producing defect-free products the first time.
- Importance: A high FPY indicates minimal waste and rework, which translates to lower costs and improved productivity.
- Application: Helps improve quality and reduce process inefficiencies.
6. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
- Definition: A composite metric that evaluates the efficiency of manufacturing equipment by considering availability, performance, and quality.
- Formula:
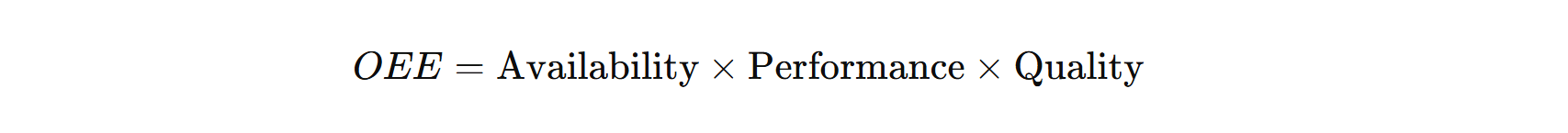
- Where:
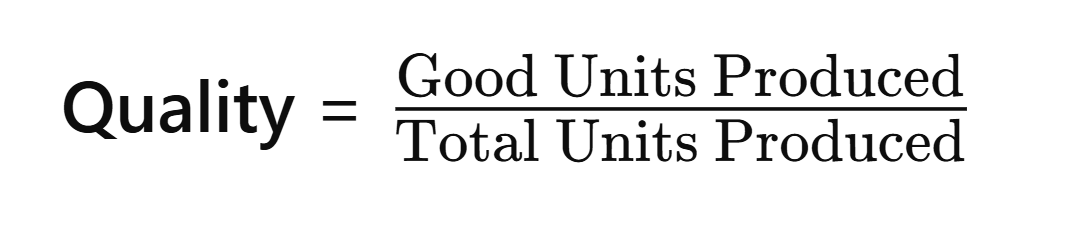
- Purpose: Measures how effectively equipment is utilized during production.
- Importance: A higher OEE value means better utilization of equipment, leading to increased productivity and lower maintenance costs.
- Application: Used to track equipment performance and identify areas for improvement in production.
7. Value Stream Mapping (VSM)
- Definition: A visual tool used to analyze and map the flow of materials and information throughout a process, identifying value-added and non-value-added activities.
- Purpose: Helps in understanding the entire flow of a process and identifying areas where waste can be eliminated.
- Importance: Enables organizations to optimize value creation by removing inefficiencies and focusing on activities that add value to the customer.
- Application: VSM helps in continuous process improvements and achieving better flow in production.
8. Kaizen (Continuous Improvement)
- Definition: A metric used to measure the incremental improvements made in a process over time, focusing on small, continuous enhancements rather than large, infrequent changes.
- Purpose: Encourages ongoing efforts to improve efficiency and quality within processes.
- Importance: A Kaizen-driven approach leads to sustainable improvements and fosters a culture of continuous learning and development.
- Application: Kaizen is used to make small, manageable changes that gradually add up to significant improvements over time.
9. Takt Time
- Definition: The amount of time available to produce a product in order to meet customer demand.
- Formula:

- Purpose: Determines the pace at which a process must operate to meet customer demand.
- Importance: Helps balance production rates with demand, ensuring that resources are efficiently allocated.
- Application: Used in production planning to avoid overproduction or underproduction.
Benefits of Lean Metrics
- Waste Reduction: Lean metrics highlight areas of waste, enabling organizations to focus on eliminating inefficiencies.
- Improved Efficiency: Monitoring metrics like cycle time, throughput, and OEE helps identify bottlenecks and streamline processes.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: By improving lead time and delivering quality products faster, Lean metrics ensure higher customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: Effective use of Lean metrics can result in lower operational costs by improving resource utilization and reducing waste.
Conclusion
Lean metrics are essential for measuring process performance and driving improvements in efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction. By focusing on waste reduction, optimizing flow, and aligning processes with customer demand, organizations can achieve significant improvements and build a sustainable culture of continuous improvement.
Commenting is not enabled on this course.